1. Deep Dream
Deep Dream 이란 인공신경망이 학습을 통해 얻은 패턴을 시각화하는 알고리즘 입니다.
사실 얻을 수 있는 효과를 본다면, 정의보다는 제목이 더 와닿습니다. Deep Dream 은 기존 이미지에 학습된 패턴을 주입하여 과잉해석하도록 유도합니다. 과잉해석 이 핵심인데요. 신경망 이 Forward propagation(순전파) 한 다음, Activations(활성화값) 에 대해 최대화가 되도록 동작합니다. 일부 레이어의 Activations 로부터 Gradient(기울기) 를 계산하는 것이죠. 그리고 최대화를 통해 얻어진 과잉해석 은 이미지를 초현실주의적 표현 으로 바꿉니다. 몽화적이죠. LSD를 한 사람들처럼요.
1.1. Beginning with Tensorflow

아, 자존심이 제법 상합니다. MATLAB 특화 카테고리에서 Python 을 먼저 사용하다니, Deep Dream 알고리즘은 구글의 알고리즘입니다. 그러니 구글에서 제공하는 TensorFlow 로 먼저 학습한 다음에 MATLAB 을 진행하겠습니다. 아래 내용부터 TensorFlow Tutorial 의 공식영문문서 의 흐름대로 진행됩니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import IPython.display as display
import PIL.Image
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
먼저 사전설정을 해줍니다.
1.2. Choose an image to dream-ify

1
url = 'https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/YellowLabradorLooking_new.jpg'
변환할 이미지url 을 설정하구요.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# Download an image and read it into a NumPy array.
def download(url, max_dim=None):
name = url.split('/')[-1]
image_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file(name, origin=url)
img = PIL.Image.open(image_path)
if max_dim:
img.thumbnail((max_dim, max_dim))
return np.array(img)
이미지를 받아와서 행렬로 전환합니다.
흑백 이미지는 행렬로서 표현가능합니다. 흑이 0, 백이 255죠. true black이 0 이라면, 회색은 한 60~180 정도 입니다.
적색을 담당하는, 녹색을 담당하는, 청색을 담당하는 흑백이미지 세개가 모이면 컬러이미지가 됩니다.
1
2
3
4
# Normalize an image
def deprocess(img):
img = 255*(img + 1.0)/2.0
return tf.cast(img, tf.uint8)
간단한 연산을 위해서 정규화를 진행합니다.
1
2
3
# Display an image
def show(img):
display.display(PIL.Image.fromarray(np.array(img)))
이미지를 표시할 함수를 정의합니다.
1
2
3
4
# Downsizing the image makes it easier to work with.
original_img = download(url, max_dim=500)
show(original_img)
display.display(display.HTML('Image cc-by: <a "href=https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Felis_catus-cat_on_snow.jpg">Von.grzanka</a>'))
그동안 def 명령어를 이용했죠. 이는 함수에 대한 정의였고 본격적으로 사용합니다.
1.2. Prepare the feature extraction model
1
base_model = tf.keras.applications.InceptionV3(include_top=False, weights='imagenet')
사전훈련된 신경망을 불러옵니다. 몽환적인 이미지를 만드는 작업은 Inceptionism 이라 부릅니다. 이 알고리즘을 발표할 때 사용한 InceptionNet 이라는 신경망과 영화 제목에서 따온 것이죠. 그래서 사전신경망 은 사용된 모델과 유사한 InceptionV3 를 불러옵니다. 다른 모델을 사용해도 되지만, 코드 구현할때 레이어 이름을 수정해야합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
# Maximize the activations of these layers
names = ['mixed3', 'mixed5']
layers = [base_model.get_layer(name).output for name in names]
# Create the feature extraction model
dream_model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=base_model.input, outputs=layers)
InceptionV3 의 구조는 아래의 이미지와 같습니다. 총 11개의 뭉치가 보이시나요? Convolution layer 가 mixed 0~10 이라는 이름으로 서로 이어져있습니다. 우리는 이 중(0~10)에서 어떤 층의 활성화값을 선택할 지 고를 수 있습니다. 예제에서는 3과 5를 선택했네요.
깊은 층을 선택하면 인간이 이해하기 쉬운 Higher-level features(고차원 특성) 가 딥드림 이미지에 자리잡습니다. 낮은 층을 선택하면 Edges, Shapes, Textures 같은 Simpler features(간단한 특성)가 딥드림 이미지에 자리잡습니다. 그리고 깊은층을 선택할수록 기울기 계산에 시간이 걸립니다.

1.3. Calculate loss
Loss를 계산함으로서 딥드림의 문을 열어보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
def calc_loss(img, model):
# Pass forward the image through the model to retrieve the activations.
# Converts the image into a batch of size 1.
img_batch = tf.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
layer_activations = model(img_batch)
if len(layer_activations) == 1:
layer_activations = [layer_activations]
losses = []
for act in layer_activations:
loss = tf.math.reduce_mean(act)
losses.append(loss)
return tf.reduce_sum(losses)
loss 는 선택한 층(mixed3, mixed5)의 활성화값들 합입니다. 그리고 뭉치마다 규모가 다르니까, 정규화를 통해서 동일한 수준으로 맞춥니다. 마지막으로 딥드림은 기울기를 최대화하는 것이니 Gradient ascent(경사 상승법) 을 이용하여 loss 최대화를 합니다.

1.4. Gradient ascent
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
class DeepDream(tf.Module):
def __init__(self, model):
self.model = model
@tf.function(
input_signature=(
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[None,None,3], dtype=tf.float32),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[], dtype=tf.int32),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=[], dtype=tf.float32),)
)
def __call__(self, img, steps, step_size):
print("Tracing")
loss = tf.constant(0.0)
for n in tf.range(steps):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# This needs gradients relative to `img`
# `GradientTape` only watches `tf.Variable`s by default
tape.watch(img)
loss = calc_loss(img, self.model)
# Calculate the gradient of the loss with respect to the pixels of the input image.
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, img)
# Normalize the gradients.
gradients /= tf.math.reduce_std(gradients) + 1e-8
# In gradient ascent, the "loss" is maximized so that the input image increasingly "excites" the layers.
# You can update the image by directly adding the gradients (because they're the same shape!)
img = img + gradients*step_size
img = tf.clip_by_value(img, -1, 1)
return loss, img
deepdream = DeepDream(dream_model)
선택한 층의 로스를 다 계산했다면, 이제 기울기를 계산해서 원본 이미지에 덧칠하는 작업을 하겠습니다.
1.5. Main Loop
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
def run_deep_dream_simple(img, steps=100, step_size=0.01):
# Convert from uint8 to the range expected by the model.
img = tf.keras.applications.inception_v3.preprocess_input(img)
img = tf.convert_to_tensor(img)
step_size = tf.convert_to_tensor(step_size)
steps_remaining = steps
step = 0
while steps_remaining:
if steps_remaining>100:
run_steps = tf.constant(100)
else:
run_steps = tf.constant(steps_remaining)
steps_remaining -= run_steps
step += run_steps
loss, img = deepdream(img, run_steps, tf.constant(step_size))
display.clear_output(wait=True)
show(deprocess(img))
print ("Step {}, loss {}".format(step, loss))
result = deprocess(img)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
show(result)
return result
dream_img = run_deep_dream_simple(img=original_img,
steps=100, step_size=0.01)
위 run_deep_dream_simple 함수는 딱히 기술적인 내용이 없어서 설명을 넘어가겠습니다. 결론적으로 아래의 이미지를 취득할 수 있습니다.

Taking it up an octave
- 심한 노이즈
- 낮은 해상도
- 규칙적인 몽환패턴
위와 같은 이유로 딥드림이미지의 수준을 올려보겠습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import time
start = time.time()
OCTAVE_SCALE = 1.30
img = tf.constant(np.array(original_img))
base_shape = tf.shape(img)[:-1]
float_base_shape = tf.cast(base_shape, tf.float32)
for n in range(-2, 3):
new_shape = tf.cast(float_base_shape*(OCTAVE_SCALE**n), tf.int32)
img = tf.image.resize(img, new_shape).numpy()
img = run_deep_dream_simple(img=img, steps=50, step_size=0.01)
display.clear_output(wait=True)
img = tf.image.resize(img, base_shape)
img = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(img/255.0, dtype=tf.uint8)
show(img)
end = time.time()
end-start
경사 상승법에 대한 스케일을 바꿔서 여러차례 적용하는 내용입니다. 여기서 Octave 는 이미지 크기를 의미합니다.

2. MATLAB
위 내용에서는 InceptionV3 를 썼습니다. 다른 모델을 사용하면, 이름 설정 할 때 불편하다고 하더라구요. 그렇지만 MATLAB 에서는 GoogleNet 혹은 AlexNet 으로서 예제를 보여주고 있습니다.
2.1. Warm-up

딥드림을 시작하기 전에, 강아지 만 구분할 수 있는 신경망을 따로 구축했습니다. 아래의 내용을 구현할 때에는 이미지들이 들어있는 PetImages 폴더가 필요합니다. 따로 학습하지 않고 사전학습된 신경망을 불러오셔도 딥드림 이미지를 만들 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
clc, clear
imds = imageDatastore("PetImages","IncludeSubfolders",true,"LabelSource","foldernames");
[imdsTrain,imdsValid] = splitEachLabel(imds,0.7,'randomized');
imds 에는 PetImages 폴더 하위의 서브폴더 이름을 Label 로 하여서 이미지들을 불러옵니다. 전체 이미지 중에서 70%는 Train, 30% Validation 으로 사용합니다.
1
2
3
net = googlenet;
numClasses = numel(categories(imdsTrain.Labels))
inputSize = net.Layers(1).InputSize
GoogleNet 을 불러왔습니다. 그리고 Label의 개수(numClasses)를 파악하고 입력 이미지로 바꿀 사이즈도 구합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
lgraph = layerGraph(net);
[learnableLayer,classLayer] = findLayersToReplace(lgraph);
numClasses = numel(categories(imdsTrain.Labels));
newLearnableLayer = fullyConnectedLayer(numClasses, ...
'Name','new_fc', ...
'WeightLearnRateFactor',10, ...
'BiasLearnRateFactor',10);
lgraph = replaceLayer(lgraph,learnableLayer.Name,newLearnableLayer);
newClassLayer = classificationLayer('Name','new_classoutput');
lgraph = replaceLayer(lgraph,classLayer.Name,newClassLayer);
전이학습을 위해서 최종 output node가 선별할 label 수와 맞추는 작업입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
pixelRange = [-30 30];
scaleRange = [0.9 1.1];
imageAugmenter = imageDataAugmenter( ...
'RandXReflection',true, ...
'RandXTranslation',pixelRange, ...
'RandYTranslation',pixelRange, ...
'RandXScale',scaleRange, ...
'RandYScale',scaleRange);
augimdsTrain = augmentedImageDatastore(inputSize(1:2),imdsTrain, ...
'DataAugmentation',imageAugmenter);
augimdsValidation = augmentedImageDatastore(inputSize(1:2),imdsValid);
Train, Validation 에 Warping 을 해줍니다. Reflection, Translation, Scale 이 옵션입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
valFrequency = floor(numel(augimdsTrain.Files)/miniBatchSize);
options = trainingOptions('sgdm', ...
'MiniBatchSize',miniBatchSize, ...
'MaxEpochs',128, ...
'InitialLearnRate',3e-4, ...
'Shuffle','every-epoch', ...
'ValidationData',augimdsValidation, ...
'ValidationFrequency',valFrequency, ...
'Verbose',false, ...
'Plots','training-progress');
netTransfer = trainNetwork(augimdsTrain,lgraph,options);
마지막으로 Train option 을 설정해주고 학습을 시작합니다.
2.2. Visualization
학습된 뒤에는 무조건 저장하는 버릇이 있습니다.
1
save("Workspace.mat");
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
%Validation
orig = imdsValid.Labels;
preds = classify(netTransfer, augimdsValidation);
%Visulization
confusionchart(orig, preds)
cm = confusionmat(orig, preds)
학습된 신경망의 성능지표를 확인합니다. 결과는 아래와 같이 시각화됩니다.

2.3. Deep Dream
순서는 Tensor flow 에서 했던 순서를 그대로 따릅니다. 다만 MATLAB 에서는 사용하기 쉽게 많이 간략화 되어있습니다. 그러나 위 방법과는 전혀 다른 방법을 사용합니다.
1
load("WorkSpaces.mat", "netTransfer")
별도로 학습한 netTransfer 만 불러옵니다.
1
2
3
4
analyzeNetwork(netTransfer)
layer = 142;
layerName = netTransfer.Layers(layer).Name;
classes = netTransfer.Layers(end).Classes(1:end)

보이는 142 번째 레이어는 마지막 출력 레이어입니다. 이 레이어를 선택하고 현재 학습된 label 들을 불러옵니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
channels = [18 20 43 50 85 110];
netTransfer.Layers(end).Classes(channels)
I = deepDreamImage(netTransfer,layerName,channels);
figure
I = imtile(I);
imshow(I)
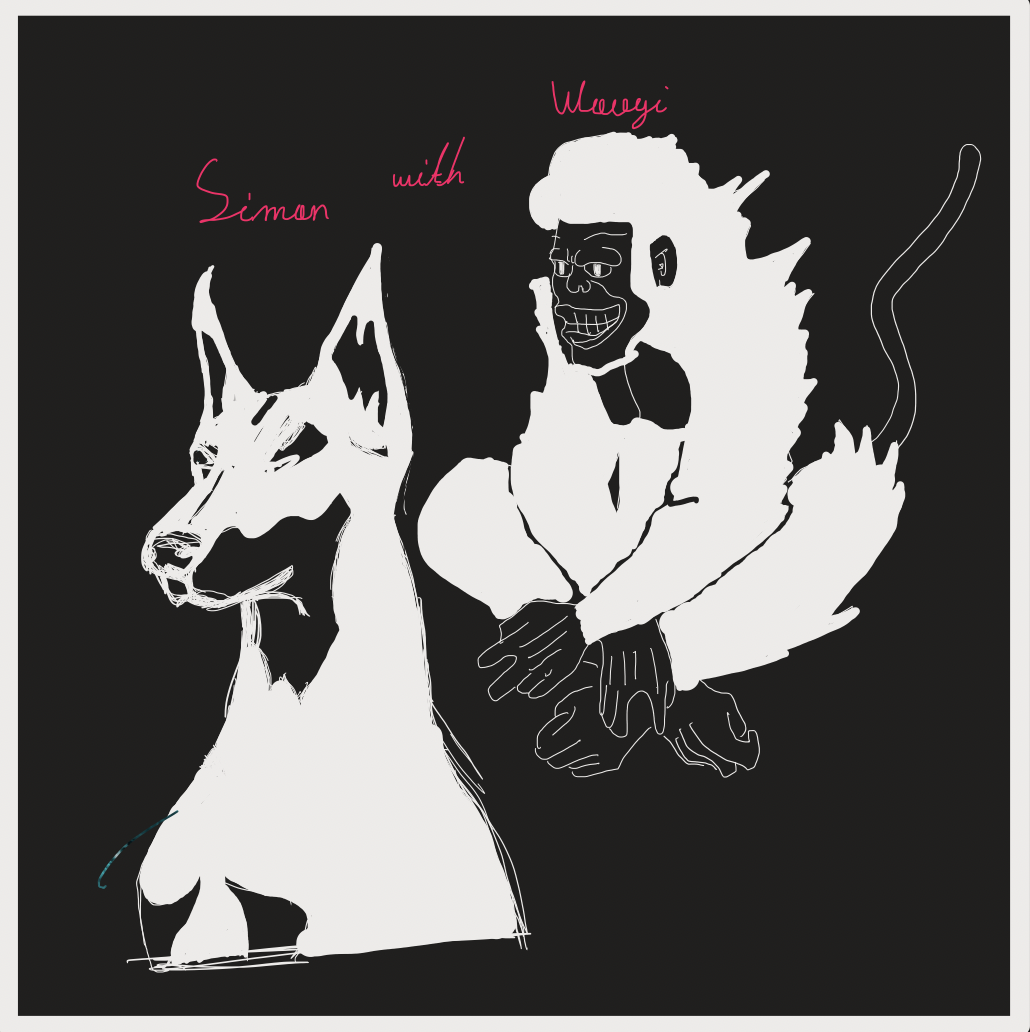
제가 좋아하는 강아지 6 종류(Chihuahua, Doberman, Leonberg, Norwich_terrier, bull_mastiff, redbone)을 선정했고 얘네가 조합된 딥드림 이미지를 생성합니다.

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
iterations = 100;
channels = 20;
I = deepDreamImage(netTransfer,layerName,channels, ...
'Verbose',false, ...
'NumIterations',iterations);
figure
imshow(I)
디테일을 살리는 작업인데요. 제가 좋아하는 도베르만에 대해서 딥드림 이미지를 생성했습니다. 아까 위 이미지와는 제법 다르게 도베르만의 모습이 많이 보이죠? 이렇게 컴퓨터에게 LSD 먹이기, 몽환적 이미지를 만드는 Deep Dream 을 마치겠습니다.

